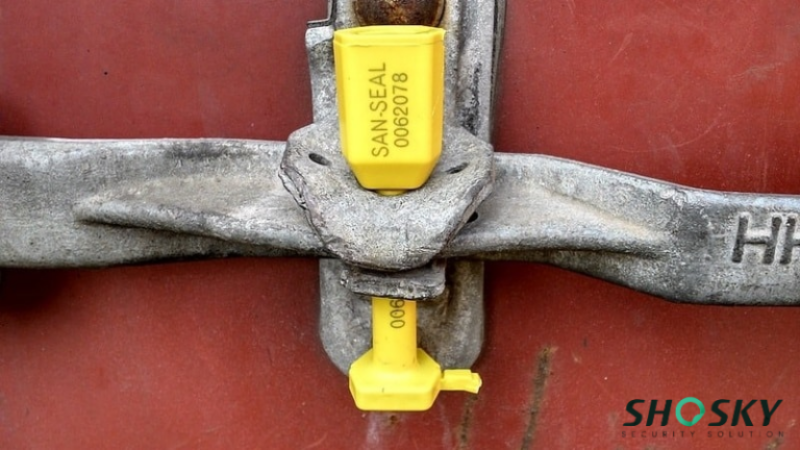
Cargo crime continues to rise across global supply chains. According to the BSI and TT Club’s 2024 Cargo Theft Report, 71% of incidents occurred while goods were in transit. Key regions like North America and parts of Asia have reported increasing use of seal tampering and unauthorized resealing as a tactic to avoid detection during inspections.
To deal with this, ISO 17712-certified security seals have become a must for shippers moving goods across borders. These seals are not just a formality—they’re part of global security programs like C-TPAT and play a direct role in customs clearance and cargo protection. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about what ISO 17712 seals are.
What Is ISO 17712 and Why Does It Matter?
ISO 17712 is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization. It defines the requirements for mechanical security seals used on cargo containers. The standard was created to help prevent tampering and unauthorized access during international shipping.
The ISO 17712 standard is backed by input from customs bodies, transportation experts, and security organizations worldwide. Its requirements are recognized globally because they create a common baseline for seal strength, durability, and tamper resistance, regardless of the country of origin or destination. This helps streamline border checks and reduce security disputes.
ISO 17712-compliant security seals are essential for programs like C-TPAT (Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism), TAPA (Transported Asset Protection Association), and the SAFE Framework from the World Customs Organization. U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). For example, mandates the use of high-security ISO 17712 seals for all C-TPAT shipments entering the United States.
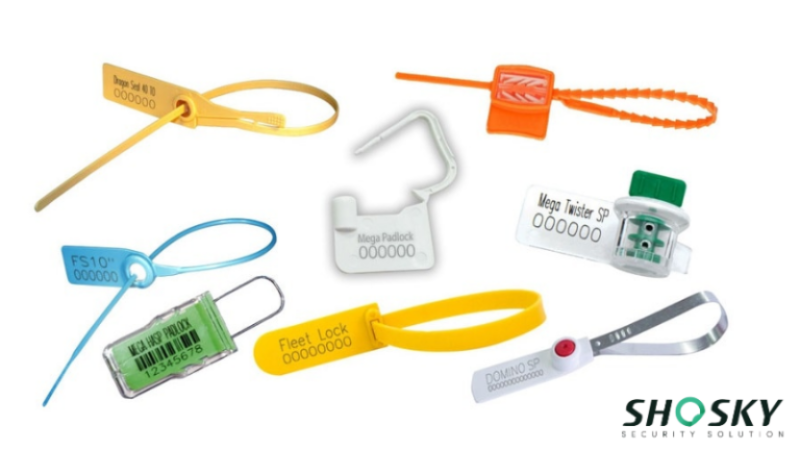
Understanding the Types of ISO 17712 Security Seals
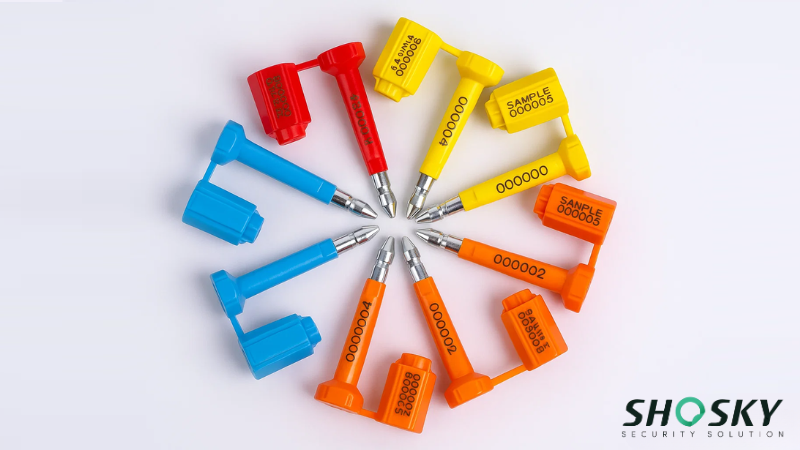
ISO 17712 classifies container seals into three categories based on strength and tamper-resistance: Indicative (C), Security (S), and High-Security (H) seals. These classes are designed to match the risk level and value of the cargo being shipped. Each type follows specific testing and marking rules to meet international standards for cargo protection. Let’s have a detailed look at them:
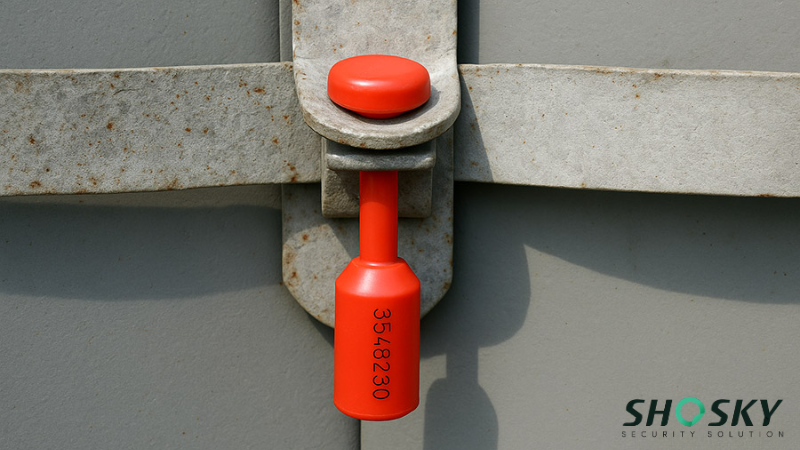
- High security seals (H class) – These barrier seals are built for international shipping. They’re made from solid metal, must pass tough tests (tensile, bending, impact), and are mandatory for C-TPAT and global customs clearance. Common types include bolt and cable seals, often used on shipping containers and trailers.
- Security seals (S class) – These seals provide visible tamper evidence but have moderate strength. They’re suitable for domestic use, bonded warehouses, and shipments with lower risk. Plastic and metal variants are both common here.
- Indicative seals (C class) – These are lightweight, typically plastic, and not designed to resist force. Instead, they help detect tampering on internal packages, low-value shipments, or inventory bins.
For example, an electronics exporter might use H-class bolt seals for intermodal containers leaving for overseas ports. A warehouse may use S-class plastic seals on pallets during local transfers. Meanwhile, C-class indicative seals could be used on internal bins for inventory control. Choosing the right seal type helps reduce risk, meet compliance standards, and avoid shipment delays at customs checkpoints.
Key Features of Compliant ISO 17712 Seals
When choosing a security seal for international shipments, meeting ISO 17712 standards isn’t just a checkbox—it’s a legal and operational safeguard. These seals are more than visual deterrents. To be certified, they must meet specific requirements for strength, testing, and traceability. Below are the three core features that define a truly compliant ISO 17712 seal.
1. Physical Features: Strength, Durability, Tamper-Resistance
Every ISO 17712 high-security seal must pass a full set of physical tests before it can be approved for use. These tests include tensile strength, bending, impact resistance, and shear force.
They’re designed to confirm that the seal can’t be removed without obvious damage or using specialized tools. This level of durability is critical for protecting cargo containers, truck trailers, and high-risk shipments in transit.
ISO 17712 testing isn’t optional—it’s a core requirement for compliance. Seals must prove they can hold up under real-world transport conditions at multiple loading points.
Without this, a seal can be easily tampered with and resealed, leaving no visible trace. Physical integrity is the first line of defense in preventing unauthorized access across the supply chain.
2. Testing Features: Certification and Lab Requirements
A seal can’t claim ISO 17712 compliance unless it has been tested by an accredited third-party laboratory. The lab must be certified under ISO/IEC 17025, which confirms it’s qualified to perform mechanical and tamper-evidence testing.
These labs follow strict procedures to validate each batch of seals, checking that the materials and construction meet required international standards. This process eliminates guesswork and adds traceability.
Along with test results, seal manufacturers must provide documentation that proves compliance. This includes testing reports, certificates of conformity, and manufacturing trace codes.
For customs officers or supply chain auditors, these documents are often required at checkpoints, especially for cargo under C-TPAT or SAFE Framework coverage. If you can’t produce a valid certification, your shipment may face delays or rejection at the border.
3. Visual Features: Serial Numbers, Tamper Indicators
One of the key parts of ISO 17712 compliance is the seal’s visual integrity. Each seal must have a unique, permanent serial number that cannot be removed, altered, or reused. This number helps customs officials and logistics staff track each unit from origin to destination.
In addition to numbering, compliant seals must include tamper-evident features that show clear signs of interference. Many high-security seals also use advanced tamper technologies like color coding, barcode labels, or laser marking to boost traceability. These visual indicators act as evidence of tampering and play a key role in protecting cargo from theft across the global supply chain.
ISO 17712:2013 vs Earlier Standards — What’s Current in 2025?
ISO 17712 has gone through a few key revisions, but the 2013 version still stands as the most widely accepted safety standard in global logistics as of 2025. While earlier versions focused mainly on tensile strength and structural integrity, the 2013 update introduced a critical layer of security: tamper-evidence testing. And this closed a major gap in cargo protection!
Here’s a quick comparison of what changed:
| Feature | Pre-2013 ISO 17712 | ISO 17712:2013 (Current in 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Strength Testing | Yes | Yes |
| Tamper-Evidence Testing | No | Yes |
| Lab Certification Required | Recommended | Mandatory |
| Serial Number Requirements | Basic | Strict |
| C-TPAT Acceptance | Not guaranteed | Fully accepted |
Customs programs like C-TPAT and AEO demand full compliance with this 2013 version, including third-party lab certification and visible tamper indicators. Sticking to pre-2013 seals could mean non-compliance, missed insurance coverage, and delayed clearance. Always verify that your seal supplier follows the current version and provides valid test reports.
When Are ISO 17712 Seals Required in International Trade?
ISO 17712 seals aren’t optional in global trade—they’re often required by law, policy, or contract. Their use goes beyond routine security. From port inspections to customs clearance, these seals play a direct role in keeping goods moving without delays. Here’s where and why they matter most.
Export Shipments via Ocean, Air, or Intermodal Freight
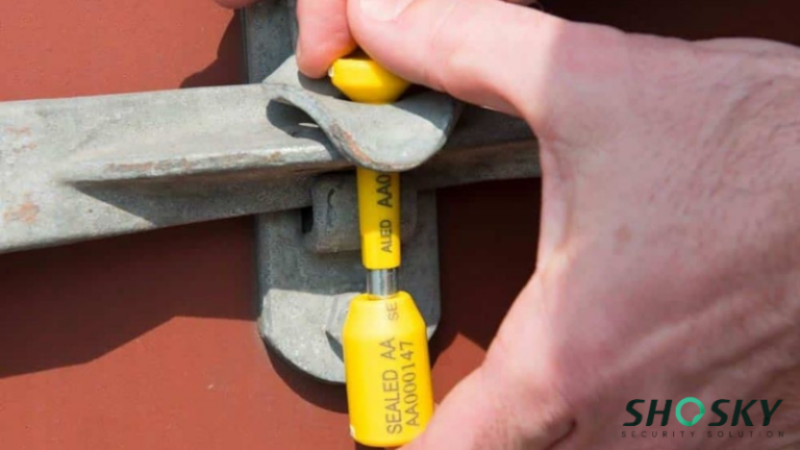
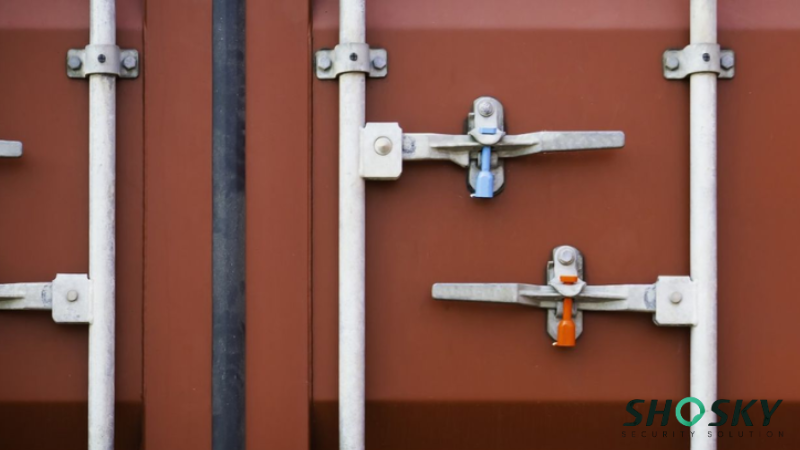
When you’re shipping goods internationally, using high-security ISO 17712 seals is a basic requirement, especially for ocean freight and intermodal transport. These seals are applied at the point of origin, such as a warehouse, airport, or port, and help keep the cargo secured throughout the journey.
Multiple handovers during transit increase the risk of tampering. A properly sealed container seal with a container security seal shows clear responsibility at each stage. If broken or missing, it signals possible tampering, which could lead to customs delays or loss-related costs.
Using the correct seal type also helps authorities in identifying any breach, making the entire process more efficient and compliant with global shipping standards.
C-TPAT and Customs Clearance Situations
Under the Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT), all containers entering the U.S. must use ISO 17712 high-security seals. These seals must meet the H classification, with proper serial numbers and compliance documents ready for verification at customs checkpoints.
Beyond the U.S., many countries aligned with the SAFE Framework also recognize ISO 17712 seals during customs clearance. Generally, using non-compliant seals can trigger manual inspections, hold-ups, or even fines, especially if cargo is flagged as high-risk or restricted.
Scenarios Where Failing to Use Compliant Seals Causes Penalties or Shipment Holds
When a container arrives without a proper ISO 17712-compliant seal, customs may view it as a potential tampering case. That can result in the shipment being held for inspection, delaying delivery and increasing port storage or demurrage costs.
Some countries use automated systems to match seal numbers with cargo declarations. If there’s a mismatch or no valid documentation, shipments may be stopped until proof of compliance is provided, causing financial and operational setbacks.
Industry-Specific Mandates (e.g., Pharma, Electronics, Defense)
Certain industries are more vulnerable to cargo tampering, theft, or counterfeiting. Sectors like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and defense often require ISO 17712 high-security seals by default, even if not explicitly enforced by customs. These seals help prevent unauthorized access and provide traceability.
In many cases, compliance isn’t just about avoiding delays—it’s part of meeting industry regulations or contract terms. For example, military shipments or medical goods often come with strict seal and packaging guidelines. Using non-compliant seals can lead to failed audits or rejected deliveries.
How to Select the Right ISO 17712 Seal for Your Shipment?
Here are five practical steps to select the right ISO 17712 seal for your shipments:
Step 1: Understand Your Cargo Type, Value, and Risk Exposure
Start by evaluating what you’re shipping. High-value items like electronics or pharmaceuticals require stronger seals, like mechanical freight container seals, than bulk goods like textiles or food products. The higher the value, the greater the need for tamper resistance and traceability.
Also consider the origin, destination, and route. Shipments passing through high-risk regions need higher security measures. Cargo theft hotspots, weak customs enforcement, or long dwell times at ports all raise the risk of tampering or pilferage.
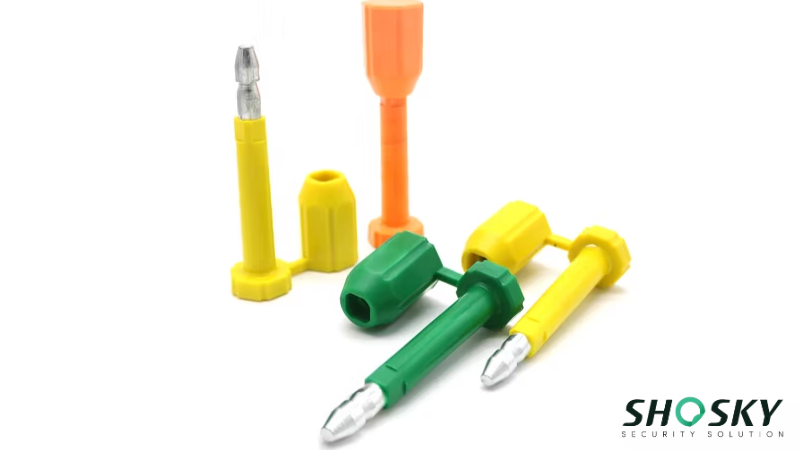
Step 2: Compare Bolt Seals and Cable Seals
Choosing the right seal type depends on the subject of your shipment and the level of security needed.
Bolt seals are built for strength and are commonly used on shipping containers and high-value cargo. However, they’re single-use, which adds to long-term costs and storage responsibility.
Cable seals give you more flexibility. You can adjust the length to secure various locking points, which makes them suitable for railcars, tankers, and truck doors. But not all cable seals are equal. In accordance with ISO 17712 standards, using a certified, high-quality option is key!
Step 3: Use Customization for Better Control
Custom-printed seals add a strong layer of shipment control. Adding your company logo, barcode, or department ID helps identify your cargo quickly and deters counterfeiting. It’s much harder for anyone to replace a seal with a generic duplicate.
Color coding is also effective for internal tracking. You can assign different colors to different cargo types, destinations, or priority levels. It simplifies sorting at warehouses and makes tampering attempts more noticeable.
Step 4: Always Buy from Verified, Compliant Suppliers
Not all seals labeled “ISO 17712” are truly certified. Only purchase from manufacturers who can show quality control and test reports from accredited labs and provide written ISO 17712:2013 certification. Without this, you risk using non-compliant seals that won’t pass customs.
Also, check if the supplier offers traceability and batch tracking. If a security incident happens, you’ll want to know exactly which batch was used and when. Serious vendors maintain production records, serialization logs, and a clear chain-of-custody.
Step 5: Review Seal Handling and Documentation Practices
Security doesn’t stop at choosing quality products—it extends to how seals are applied, tracked, and removed. Your team is responsible for handling seals with care at every step. Train staff to attach seals correctly and check for damage or breakage.
Seal numbers should always be recorded in the following documents: the Bill of Lading, shipment checklists, and any carrier logs. At the destination, receiving teams must verify seals before removal. If a seal appears tampered with or mismatched, the cargo should be held and inspected. Failing to do so can lead to serious consequences, including disputes with customers and customs delays.
Real-World Use Cases of ISO 17712 Seals
Industries with high-value or sensitive cargo rely on ISO 17712 Seals to protect their supply chains from theft, delays, and compliance issues. Below are some real examples of how different sectors use ISO 17712-compliant seals in their operations:
- Automotive OEMs – Toyota, Volkswagen, Ford, Hyundai, and GM use heavy-duty H-seals when moving engine blocks and transmissions between Asia and Europe. These seals protect shipments during long, multi-border routes.
- Retail Distributors – Walmart, IKEA, Costco, H&M, and Target apply ISO 17712 cable seals to bonded containers moving between warehouses. They help prevent tampering during inland transport and customs checks.
- Medical Exporters – Pfizer, Moderna, Bayer, GSK, and Novartis ship temperature-sensitive or controlled drugs using bolt seals with serial numbers. These seals support FDA rules and traceability.
- Electronics Brands – Samsung, Apple, Dell, Lenovo, and Sony seal tech shipments with barcode-tagged cable seals. This helps track containers and flag tampering in risky transit zones.
Each industry uses various types of seals that match its cargo sensitivity, shipping route, and legal requirements. These seals are more than just locks—they’re tools that support compliance, reduce risk, and boost efficiency.
FAQs
Is ISO 17712 a general requirement for all international shipments?
No, ISO 17712 seals are not required for all international shipments. They are only required for container cargo in high-security or customs-controlled routes.
What’s the difference between ISO and C-TPAT requirements?
ISO sets the seal standard; C-TPAT enforces it for U.S.-bound shipments.
Where can I buy high-security certified ISO 17712 seals?
You can purchase certified ISO 17712 seals from trusted security seal manufacturers or suppliers like Shosky Security.
Conclusion
ISO 17712 seals aren’t just about ticking boxes—they’re about protecting your cargo, brand, and bottom line. If you ship containers across borders, especially to the U.S., using certified high-security tamper-evident solutions and seals is no longer optional.
Whether you’re in automotive, retail, or pharma, the right seal helps prevent losses and clears customs faster. Know the rules, choose the right type, and work with trusted suppliers.
Protect Your Cargo with ISO 17712 Security Seals from Shosky
Shosky Security offers ISO 17712:2013 certified tamper-evident seals that meet today’s global shipping standards. We help you stay compliant, reduce delays, and protect your cargo from start to finish. Need certified seals fast? Contact us now!