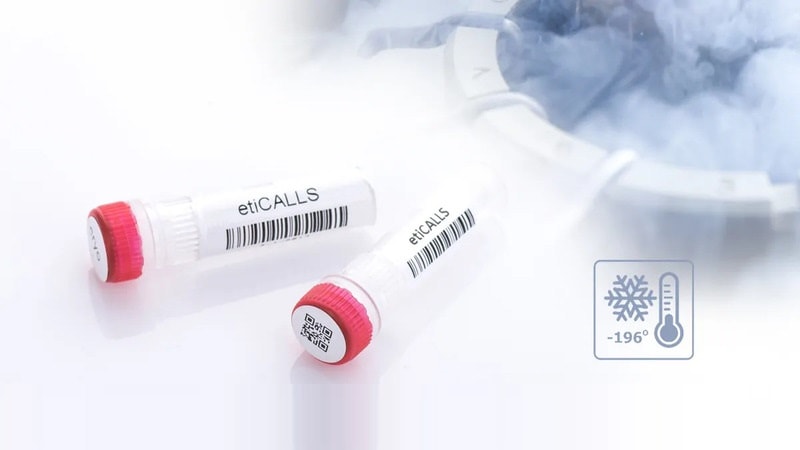
The global cold chain logistics market, valued at billions of dollars, is constantly in battle with tampering, theft, and counterfeiting. With temperature-sensitive products requiring specialized handling and storage conditions, traditional security measures often fall short of providing the comprehensive protection needed in these complex supply chains.
In this regard, modern tamper-evident label solutions have emerged as major advancements in this space, offering innovative ways to secure cold chain shipments. In this article, we’ll discuss their role in protecting temperature-sensitive goods, ensuring compliance, and strengthening overall supply chain integrity. Let’s get to it.
Why Standard Security Labels Fail in the Cold Chain?

To choose the right solution, you must first understand the physics behind why standard labels fail. Failure of a security label in a refrigerated environment is usually due to thermodynamic adhesion.
The “Glass Transition” of Adhesives
Standard pressure-sensitive adhesives (used in office supplies or standard shipping labels) are viscoelastic liquids. They work by “wetting out” or flowing into the microscopic texture of the package surface to create a bond.
However, every adhesive has a Glass Transition Temperature (Tg). When the ambient temperature drops below this Tg point, the adhesive stops acting like a sticky liquid and turns into a hard, non-tacky solid.
In this state, it loses its ability to bond. If a standard label is applied in a cold room, it simply won’t stick. If it is applied at room temperature and then frozen, the adhesive may crystallize and pop off as the packaging material shrinks in the cold.
The Barrier of Condensation and Frost
Moving goods between temperature zones (e.g., from a loading dock to a refrigerated truck) creates condensation. Even a microscopic layer of water or ice crystals on a package surface acts as a barrier.
Standard water-based acrylic adhesives cannot penetrate this moisture barrier. They sit on top of the water droplets rather than the package surface. When the water eventually freezes or evaporates, the label falls off.

Furthermore, moisture can “deaden” the release coating used in tamper-evident labels. Even if the label sticks, the moisture may prevent the “VOID” pattern from separating correctly when peeled, rendering the security feature useless.
Substrate Shrinkage
Materials react to cold by contracting. Plastic shrink wrap, corrugated cardboard, and glass vials all shrink at different rates in freezing temperatures.
If the face stock of the label (the top material) is rigid (like standard paper or thick vinyl) and the adhesive is frozen solid, the label cannot flex with the shrinking package. This stress causes “flagging” (lifting at the corners) or “tunneling,” breaking the security seal without human intervention.
3 Key Tamper-Evident Label Types for Refrigerated & Frozen Goods
To combat these issues, you need labels engineered with specialized face stocks and aggressive adhesives.
1. Cryogenic / Freezer-Grade Void Labels

These are the gold standard for high-value pharmaceutical and biotech shipments. They utilize aggressive, solvent-based acrylic adhesives or specialized hot-melt rubber compounds designed to maintain high tack (stickiness) even at extreme lows.
For their face stock, they typically use flexible synthetic films like polypropylene or polyethylene that do not become brittle in the cold.
- The Mechanism: Unlike water-based adhesives, solvent-based options flow aggressively into the substrate surface and resist freezing down to -40°C, -80°C, or even -196°C (liquid nitrogen environments).
- Best Application: Vaccines, blood plasma, clinical trial samples, and high-value frozen food exports (like seafood or meat).
2. Moisture-Resistant Destructible Labels
Standard destructible vinyl, the material of destructible labels, works by being incredibly fragile; it shatters like an eggshell when removed. However, standard “eggshell” paper turns to mush when it gets wet from condensation. Cold chain destructible labels utilize fragmentable synthetic films (such as brittle acetate or modified polystyrene).The
- The Mechanism: These materials are waterproof and dimensionally stable. They will not warp or dissolve when exposed to high humidity or direct condensation. However, the structural integrity is weak enough that any attempt to lift the label causes it to chip away in tiny fragments.
- Best Application: Chilled beverages, dairy products, food delivery containers, and meal kit logistics where condensation is guaranteed.
3. Temperature Indicator Security Labels

For the ultimate in compliance, some advanced labels combine tamper evidence with temperature monitoring. These labels feature a chemical indicator that changes color irreversibly if the temperature deviates from a set range (e.g., rising above 8°C), while the label itself provides proof against physical tampering.
- The Mechanism: These labels contain a chemical window that changes color irreversibly (e.g., from white to red) if the temperature exceeds a safe threshold (Time-Temperature Integrators or TTIs). This is combined with a tamper-evident base.
- Best Application: Biologics and sensitive chemical reagents, where “safety” means both authenticity and efficacy.
How to Choose the Right Label for Your Cold Chain Logistics?
Selecting a cold chain label is more complex than buying standard office supplies. You must analyze your specific logistical workflow. Use this framework to determine your requirements.
Factor 1: Application Temperature vs. Service Temperature
This is the most common technical specification that buyers misunderstand.
Application Temperature
The temperature of the environment at the moment the label is stuck onto the box. Here are two scenarios:
- Scenario A: You label the box at room temperature (+20°C) and then put it in the freezer. (Easier, requires standard aggressive adhesive).
- Scenario B: You are labeling a box that is already frozen (-20°C) inside a freezer. (Hardest scenario, requires specialized “All-Temp” or “Deep Freeze” adhesives designed to grip frozen surfaces instantly).
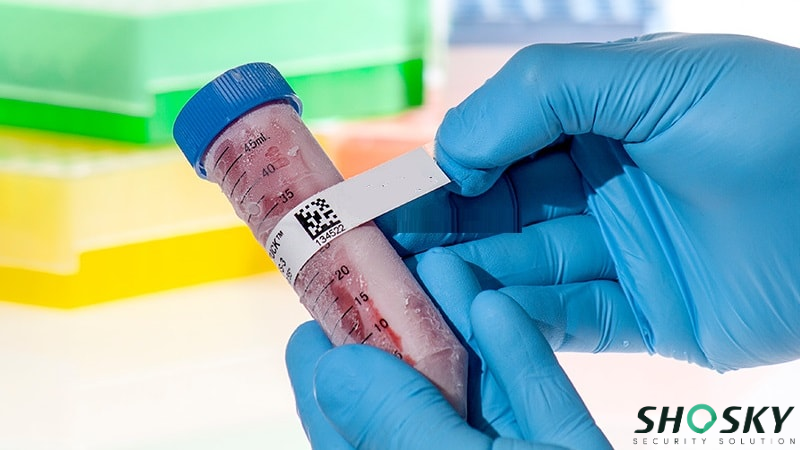
Service Temperature
The temperature range the label must endure after it has been applied.
If you need to store in liquid nitrogen, a standard “freezer label” will fail. You need a designated Cryogenic label.
Factor 2: The Substrate (Surface Energy)
What are you sticking the label to? Here are some applications that you will probably stick your label on :
- Corrugated Cardboard: Porous and absorbs moisture. In freezers, it can become icy. Requires a high-coat-weight adhesive to flow into the fibers.
- Shrink Wrap / Plastic Pallets: These are “Low Surface Energy” (LSE) plastics. They are slippery and hard to stick to, especially when cold. Standard adhesives will slide off. You need a high-tack rubber or modified acrylic adhesive.
- Glass Vials: Smooth but curved. Rigid labels will lift at the edges (flagging). You need a flexible film face stock.
Factor 3: Security Level Requirements
Different products require varying levels of security based on their value and sensitivity.
High Risk (Pharma/Electronics)
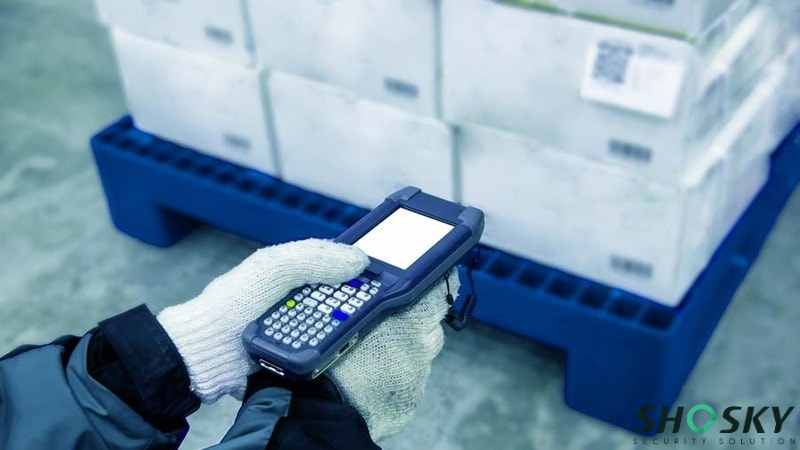

For high-risk industries like pharma and electronics, they require Total Transfer void labels (which leave a messy residue on the box to ruin it) or High-Residue seals. Customization with holograms and serialization is mandatory.
Medium Risk (Food/Retail)
For medium-risk industries like food and retail, non-residue void labels are often preferred for reusable crates (totes), so the crate can be cleaned and reused without scraping off glue.
Regulatory Compliance for Cold Chain Logistics
In cold chain logistics, security is not just about loss prevention; it is a regulatory requirement. Using the correct tamper-evident labeling is often a prerequisite for doing business in regulated sectors.
Good Distribution Practice (GDP)
GDP guidelines (enforced by the EMA in Europe and the WHO globally) mandate that medicines remain secure and stable during transport.
The Requirement: An interoperable, electronic tracing of products at the package level.
The Label Solution: Cold chain security labels are now the carrier for this data. Shosky can print serialized 2D barcodes or QR codes directly onto the tamper-evident label. This links the physical security (the seal) with the digital truth (the FDA database). If the seal is broken, the digital identity is compromised.
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 & DSCSA

The US Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) is driving the industry toward full unit-level traceability.
The Requirement: An interoperable, electronic tracing of products at the package level.
The Label Solution: Cold chain security labels are now the carrier for this data. Shosky can print serialized 2D barcodes or QR codes directly onto the tamper-evident label. This links the physical security (the seal) with the digital truth (the FDA database). If the seal is broken, the digital identity is compromised.
FSMA (Food Safety Modernization Act)
Under the FSMA’s “Mitigation Strategies to Protect Food Against Intentional Adulteration,” companies must implement food defense plans.
The Requirement: Vulnerability assessments to identify points where intentional contamination could occur.
The Label Solution: Tamper-evident tape on pallet wrap or security labels on clamshell containers are recognized mitigation strategies to prevent “intentional adulteration” during transit.
How to Implement Tamper-Evident Labeling in Cold Chain Logistics
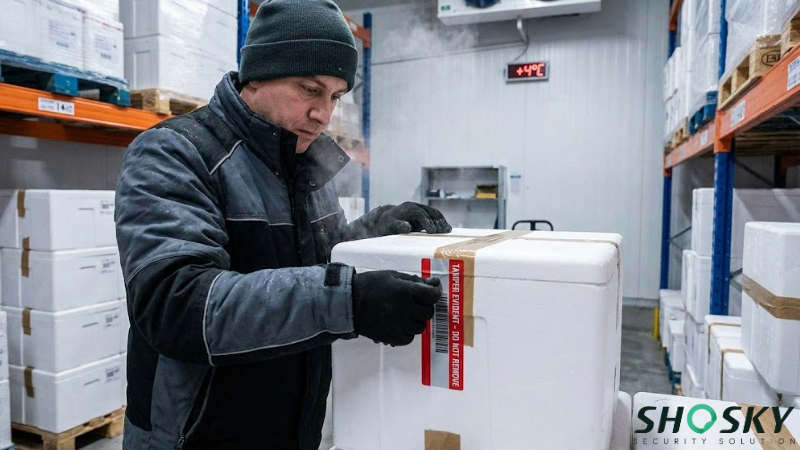

Even the most expensive cryogenic label will fail if applied incorrectly. Warehouse managers should incorporate the following Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for their packing teams:
1. The “Wipe-Down” Protocol
Moisture is the enemy. Even if a box looks dry, it may have a thin film of frost. Before applying the label, staff must wipe the application area with a dry, lint-free cloth or a squeegee. This removes surface frost and dust, allowing the adhesive to contact the substrate directly.
2. Pressure Application Technique
Most cold chain adhesives are pressure-sensitive (PSA). They utilize microscopic capsules of adhesive that must be crushed to activate the bond. Do not just lightly pat the label. Apply firm pressure across the entire surface of the label, especially the edges. Use a roller tool if possible. This “wets out” the adhesive, forcing it into the surface texture before it freezes.
3. Managing “Dwell Time”
Adhesives need time to flow and set (cure). If your workflow allows, apply the security labels at room temperature and allow them to cure for 24 hours before moving the product into the deep freeze. This allows the bond to reach 100% strength. If labeling inside a freezer, ensure the label stock is kept warm (e.g., inside a jacket or heated dispenser) until the moment of application.
4. Overlap for Shrink Wrap
When securing pallets wrapped in stretch film, the film itself is unstable and shifts. Do not rely on the label sticking only to the plastic. Use tamper-evident tape wrapped entirely around the pallet, overlapping onto itself. Adhesive bonds to its own backing better than it bonds to cold plastic.

Benefits of Specialized Cold Chain Labeling
Investing in specialized labeling offers ROI beyond simple theft prevention.
Brand Protection & Consumer Confidence
In the era of social media, a photo of a tampered food delivery or a spoiled vaccine vial can destroy a brand’s reputation overnight. A visibly secure, intact seal is a marketing asset that screams “Quality.”
Liability Reduction
When goods arrive damaged or missing, the liability battle begins between the manufacturer, the logistics provider, and the retailer. A serialized, tamper-evident seal provides forensic evidence of where the chain was broken, protecting honest parties from liability claims.
Reduction in “False Positives”
Standard labels often fall off due to cold, leading to false alarms of tampering. This wastes money on investigations and replacement products. High-performance cold chain labels stay put, ensuring that a broken seal truly indicates a security breach.
FAQs
Q1: Can tamper-evident labels be used for food packaging?
Yes, they help prevent contamination and ensure product integrity, especially for sealed containers and perishables.
Q2: Does law require tamper-evident labels for pharmaceutical shipments?
Yes, many regulations mandate their use to protect drug safety and prevent unauthorized access.
Q3: How do tamper-evident labels work in cold chain security?
They show visible signs of tampering and use adhesives that withstand temperature changes and moisture.
Q4: What is the difference between “Cryogenic” and “Freezer” labels?
“Freezer” labels are typically rated for -20°C to -40°C (standard food/pharma storage). “Cryogenic” labels are rated for -80°C to -196°C (dry ice, liquid nitrogen) and use entirely different face stocks (like nylon cloth or specialized poly) to prevent shattering at those extreme temperatures.
Q5: Can I use standard “Void” tape for refrigerated pallets?
No. Standard packing tape adhesive hardens and loses tack below 0°C. It can be peeled off without triggering the “void” message.
Conclusion
Tamper-evident label solutions are a vital component of cold chain logistics security, ensuring that temperature-sensitive products remain safe and intact from origin to destination. As cold chain logistics continue to evolve, investing in advanced tamper-evident labeling solutions can enhance security, streamline operations, and build trust with consumers and regulatory bodies!
Secure Your Cold Chain with Shosky Security Today!
At Shosky Security, we provide advanced tamper-evident labels, tapes, and seals designed to meet the unique challenges of cold chain logistics. Contact us today to explore our customizable security labels and enhance your cold chain protection!